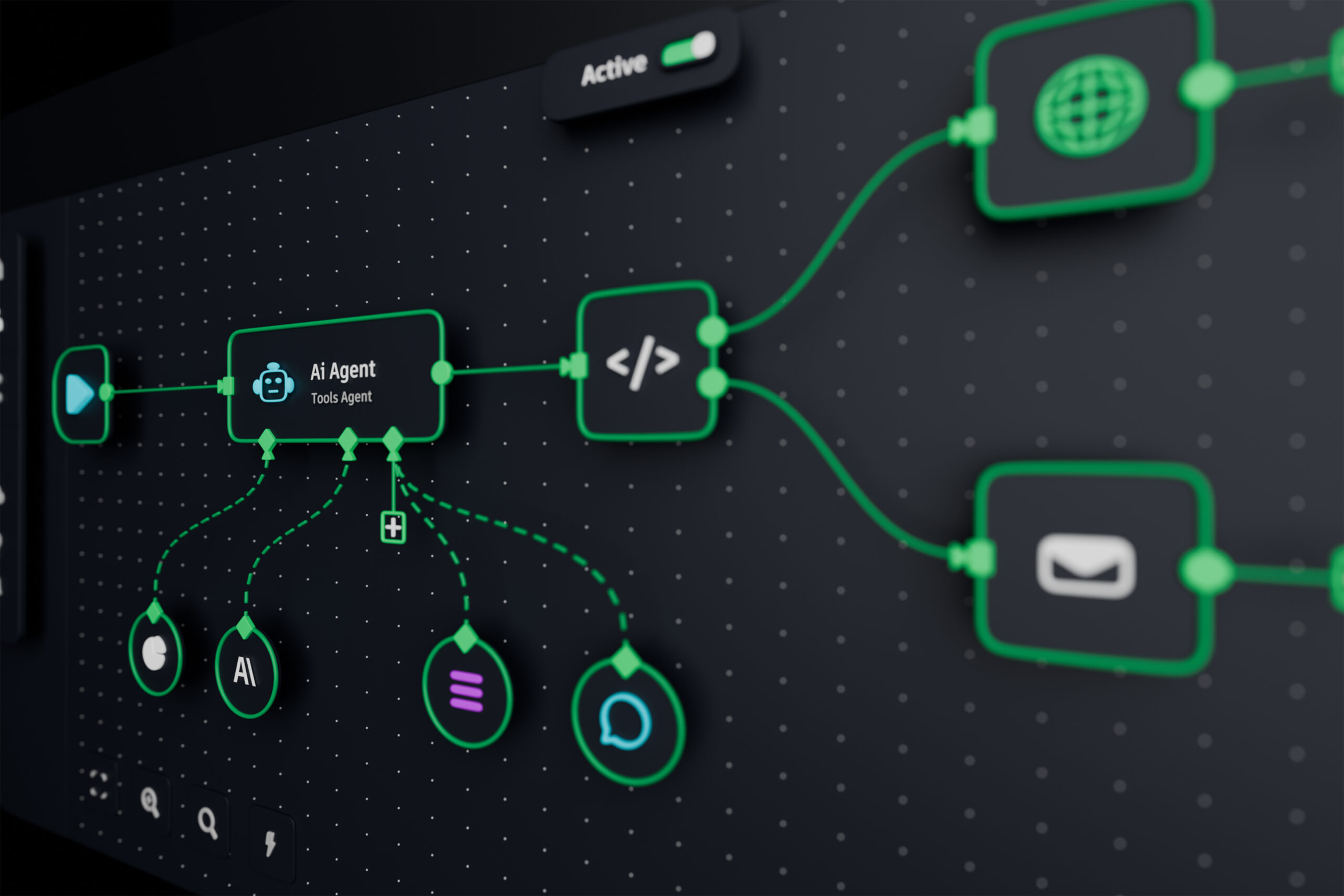
Selecting the best CRM system for your healthcare organization is a challenge with real consequences. Each option affects patient satisfaction, data security, and care coordination. With so many choices available, it is easy to feel uncertain about which features truly make a difference for your providers and patients.
This list gives you clear, actionable insights directly from proven healthcare CRM models. You will discover real approaches that improve decision making, care team collaboration, and long-term patient loyalty.
Get ready to learn the practical strategies and system designs top healthcare providers in Saudi Arabia and UAE are using today. What you find in these numbered sections could transform the way your organization delivers care and builds patient trust.
Table of Contents
- 1. Operational CRM for Streamlined Patient Interactions
- 2. Analytical CRM Enhancing Data-Driven Decisions
- 3. Collaborative CRM for Improved Care Coordination
- 4. Strategic CRM Supporting Long-Term Patient Loyalty
- 5. Cloud-Based CRM Solutions for Scalable Deployment
- 6. On-Premise CRM for Enhanced Data Security
- 7. Industry-Specific CRM for Healthcare Needs
Quick Summary
| Key Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Implement Operational CRM for Efficiency | Automating patient interactions can improve workflows and reduce administrative burdens, freeing staff to focus on care. |
| 2. Use Analytical CRM for Data Insights | Analyzing patient data helps identify trends, optimize care strategies, and reduce costs through evidence-based decisions. |
| 3. Enhance Collaboration with Collaborative CRM | A shared system for providers improves communication and care coordination, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction. |
| 4. Build Loyalty with Strategic CRM | Personalized engagement fosters patient loyalty, encouraging them to return and recommend your services to others. |
| 5. Choose Industry-Specific CRM Solutions | Tailored healthcare CRMs support unique workflows and compliance needs, improving user adoption and operational efficiency. |
1. Operational CRM for Streamlined Patient Interactions
Operational CRM forms the backbone of modern patient engagement in healthcare. This system type automates and manages the day-to-day interactions between your staff and patients, transforming how appointments are scheduled, communications are handled, and follow-ups are executed.
In healthcare settings across Saudi Arabia and UAE, operational CRM directly impacts patient satisfaction and operational efficiency. When a patient calls your hospital or clinic, an operational CRM system ensures that their information is instantly available to whoever answers the phone. Your receptionist sees their complete history, recent visits, medications they are taking, and any previous concerns. This eliminates the frustration of patients repeating information and creates a seamless experience from the moment they contact your facility.
The core function of operational CRM is automation of routine tasks. Rather than staff members manually scheduling appointments, sending reminder emails, or logging patient interactions, the system handles these workflows automatically. Your team can set up rules that trigger specific actions when patients meet certain conditions. For example, when a patient books a surgery appointment, the system automatically sends confirmation emails, schedules pre-operative testing reminders, and alerts the surgical team. This reduces human error by approximately 40 percent and frees your staff to focus on more complex patient care activities.
One of the most practical benefits you will experience is improved appointment management. Healthcare CRM insights show that operational systems reduce no-show rates significantly through automated reminders sent via SMS and email. Your system can send a reminder 48 hours before the appointment, then another reminder the morning of the appointment. Patients who receive these timely notifications are far more likely to attend, which improves your facility’s capacity utilization and reduces revenue loss from empty time slots.
Operational CRM also creates a unified communication channel. Instead of patient information scattered across multiple systems like email, paper charts, and separate scheduling software, everything lives in one place. When a patient calls with a question about their prescription refill, your pharmacist can instantly see the conversation your clinical coordinator had with that patient three days earlier. This continuity of communication prevents misunderstandings and ensures consistent care quality.
Consider a specific scenario in a Dubai healthcare facility. A diabetic patient books a follow-up appointment after an initial consultation. The operational CRM automatically triggers a workflow that sends the patient educational materials about diabetes management, schedules lab work reminders, and alerts their physician three days before the appointment to review the patient’s blood glucose readings. The physician then comes to the appointment fully prepared. Compare this to a manual process where these tasks fall through cracks and appointments become reactive rather than proactive.
Another critical advantage is that operational CRM captures valuable behavioral data. Each patient interaction is logged automatically. Your system learns which patients are at risk of missing appointments, which ones have billing issues that need proactive resolution, and which patients consistently request specific providers. This data helps you optimize operations. You can staff more personnel on days when high-risk appointment groups are scheduled. You can reach out to patients with billing concerns before they become collection issues.
For healthcare CIOs managing large organizations in the region, operational CRM reduces the burden on support staff. Instead of your team spending hours on manual data entry and appointment confirmation calls, your system works 24/7. This is particularly valuable in a healthcare environment where patient volume is high and staff capacity is already stretched thin. The investment in operational CRM implementation often pays for itself within 18 months through reduced administrative labor costs alone.
Implementing operational CRM successfully requires careful attention to workflow design. Your team needs to map out exactly how patient interactions flow through your organization and then configure the system to match those workflows. This is where low-code platforms become invaluable. Rather than waiting months for custom software development, platforms like Cortex allow your team to design, test, and modify workflows in weeks. You can make changes in real-time without system downtime, which means you can continuously optimize how your CRM handles patient interactions as you learn what works best in your specific healthcare context.
Pro tip: Start your operational CRM implementation by focusing on your highest-volume patient interaction process first, whether that is appointment scheduling, patient intake, or post-discharge follow-ups. Prove the value in that single workflow before expanding to others, and you will build internal momentum and user adoption that makes subsequent implementations much smoother.
2. Analytical CRM Enhancing Data-Driven Decisions
Analytical CRM transforms your healthcare organization from reactive to proactive by converting massive amounts of patient data into actionable intelligence. Instead of simply storing patient information, this system type analyzes patterns, predicts outcomes, and reveals opportunities for improving care delivery.
Where operational CRM handles day-to-day patient interactions, analytical CRM looks at the bigger picture. Your system aggregates data from electronic health records, patient demographics, treatment outcomes, appointment history, and billing information. This consolidated view reveals trends that individual data points would never show. You might discover that patients taking a specific medication combination have a 35 percent higher readmission rate, or that patients who attend a particular wellness program reduce emergency room visits by 22 percent. These insights drive evidence-based decisions that improve outcomes and reduce costs.
In healthcare systems across Saudi Arabia and UAE, analytical CRM addresses a critical challenge. Your organization collects vast amounts of data daily, yet much of it remains siloed and underutilized. Analytical CRM breaks down those silos. Data-driven decision making in clinical informatics shows that when healthcare providers combine patient data from diverse sources with advanced analytics, they identify population health trends more accurately and allocate resources more efficiently.
The mechanics of analytical CRM rely on several powerful techniques. Machine learning algorithms detect hidden patterns in your patient population. If you have data on 50,000 patients, manual analysis would take your team months to spot meaningful correlations. A machine learning model can process that data in hours and identify patient segments that require intervention. Data visualization tools then present these findings in charts and dashboards that your clinical and operational leaders can understand instantly. Instead of staring at spreadsheets with thousands of rows, your team sees visual representations that make patterns obvious.
Consider a practical example from a Saudi healthcare facility managing a large diabetic patient population. Your analytical CRM analyzes medication adherence patterns, blood glucose readings, dietary compliance data from patient surveys, and appointment attendance records. The system identifies that patients who attend group education sessions every month have a 40 percent better glucose control outcome than those who do not. Your system flags patients who have never attended these sessions and alerts your care coordinators. These coordinators can then reach out proactively with invitations. This targeted intervention approach achieves better outcomes because you focus resources where they will have the greatest impact.
Another powerful application is predictive analytics. Your analytical CRM can predict which patients are at highest risk for hospital readmission within 30 days of discharge. These predictions allow you to intervene before readmission occurs. You might assign a nurse to call high-risk patients every few days, arrange home health visits, or adjust medications proactively. Preventing a single hospital readmission saves your organization thousands of dollars and prevents patient suffering. When analytical CRM helps you prevent just 10 to 15 readmissions per month, the return on investment becomes compelling.
Staff performance and resource optimization also benefit from analytical CRM. Your system can analyze which physicians have the best patient satisfaction scores, which departments have the highest complication rates, and which clinics are most efficiently organized. This data supports performance conversations and helps you identify best practices to share across your organization. You might discover that one clinic schedules patients in a way that minimizes wait times, or that one department has developed a protocol that reduces infections. When you can identify and replicate these successes, your entire organization improves.
Implementing analytical CRM successfully requires investment in both technology and talent. You need the platform itself, but you also need people who understand how to design analytics, interpret results, and translate data insights into action. This is where a low-code platform like Cortex becomes valuable. Your team does not need advanced programming expertise to build data models and visualizations. The platform allows business analysts and healthcare professionals to design analytics workflows without coding. You can quickly prototype an analysis, test it with real data, and refine it based on results. This speed and flexibility mean you can respond to emerging clinical questions within weeks rather than waiting months for custom software development.
One important consideration for healthcare CIOs is data governance and privacy. Analytical CRM involves analyzing sensitive patient information, which requires rigorous security controls and compliance with healthcare regulations. Your implementation must include proper data anonymization for certain analyses, audit trails that show who accessed what data and when, and encryption of data both in transit and at rest. The good news is that modern analytical CRM platforms are designed with healthcare compliance in mind. HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory requirements are built into how these systems handle data.
The competitive advantage of analytical CRM should not be underestimated. Healthcare organizations that use analytics to optimize their operations, improve clinical outcomes, and reduce costs simply outperform those that rely on intuition and historical practice patterns. Patients notice the difference. Staff members feel more supported. And your financial performance improves. Your analytical CRM becomes the engine that drives continuous improvement across your entire organization.
Pro tip: Start your analytical CRM journey by identifying one high-impact clinical or operational problem that your leadership cares about solving, then build your first analytics initiative around that problem rather than trying to analyze everything at once, and this focused approach will generate visible results that build support for expanding analytics across your organization.
3. Collaborative CRM for Improved Care Coordination
Collaborative CRM breaks down the walls between departments and providers, enabling your entire care team to work from a single source of truth. This system type transforms how physicians, nurses, specialists, therapists, and support staff communicate and coordinate patient care across your organization.
In traditional healthcare settings, care coordination happens through fragmented communication. A patient sees their primary care physician who refers them to a cardiologist. The cardiologist orders tests but may not see the latest laboratory results from the primary care clinic. The patient receives conflicting instructions from different providers. Meanwhile, a hospital readmission specialist has no idea that this patient was recently discharged and needs follow-up care. Collaborative CRM eliminates these gaps by creating integrated workflows where all providers access the same patient information simultaneously.
The core benefit of collaborative CRM is reduced care fragmentation. Collaborative care models demonstrate that when healthcare providers coordinate through shared systems, clinical outcomes improve significantly and health system efficiency increases. Your collaborative CRM becomes the digital infrastructure that makes coordinated care possible. Every provider on the care team sees the same updated patient information, shared care plans, and communication threads. When a patient calls with a concern, any staff member who answers the phone can understand the full context of their care journey.
Consider how this works in practice at a large hospital system in Dubai. A patient with diabetes, hypertension, and mild kidney disease needs coordinated care from an endocrinologist, nephrologist, and cardiologist. Without collaborative CRM, each specialist maintains separate records and may prescribe medications without fully understanding what the other specialists are doing. With collaborative CRM, the system displays an integrated view of the patient’s current medications, recent test results from all specialties, and a shared care plan that all three specialists have reviewed and agreed upon. When the nephrologist orders a medication adjustment, the system alerts the cardiologist and endocrinologist that a change has been made. The cardiologist can immediately assess whether this change affects the patient’s blood pressure management. Complications are prevented because coordination happens in real-time rather than through delayed phone calls and faxes.
Collaborative CRM also addresses accountability in care delivery. When you have a shared system, it becomes clear who is responsible for each aspect of patient care. Your system assigns tasks to specific team members with due dates. A care coordinator might be assigned to schedule the patient’s follow-up appointment with the nephrologist, while a nurse might be assigned to call the patient to ensure they understand their medication changes. When these tasks are tracked in the CRM, nothing falls through the cracks. Managers can generate reports showing which team members consistently complete their care coordination tasks on time and which ones need additional training or support.
Implementing collaborative CRM successfully requires rethinking how your providers work together. You must establish shared care planning processes where providers from different specialties and departments actually collaborate on treatment plans before they are implemented. Your CRM workflow should reflect this collaborative process. For example, when a patient is admitted for a procedure, your system might automatically notify all relevant specialists that the patient is in the hospital. Each specialist can review the case, add their input to the care plan, and see what others have suggested. This coordination happens before the patient even arrives on the unit, rather than coordinating care reactively during the hospital stay.
In healthcare organizations across Saudi Arabia and UAE with multiple campuses or clinics, collaborative CRM becomes even more critical. Your physicians might be geographically distributed, yet they need to coordinate care seamlessly. A patient might visit your clinic in Riyadh one week and your hospital in Jeddah the next week. Collaborative CRM ensures that both locations have access to the same information and that care coordination continues regardless of where the patient receives care. Communication happens through the CRM rather than through phone calls and emails that get lost or delayed.
Effective collaboration reduces care fragmentation and errors by ensuring all providers and patients have clear, shared expectations and timely access to updated care information, thus improving patient safety and outcomes.
Another powerful aspect of collaborative CRM is its ability to improve patient engagement. Your system can include patient portals where patients see their care plan, view messages from their care team, and understand what each provider is doing. When patients understand that their diabetes management plan coordinates with their heart disease management, they feel more confident in their care. When they receive clear, consistent instructions from their entire care team rather than conflicting advice, they are more likely to follow through with treatment plans.
For healthcare CIOs implementing collaborative CRM, workflow design is paramount. You need to map out exactly how your care coordination should work for different patient populations and conditions. A patient with chronic disease management needs different coordination workflows than a patient preparing for surgery. Your low-code platform like Cortex allows your team to design these workflows collaboratively with your clinical staff. Rather than dictating how care coordination should work, your platform enables clinicians to design workflows themselves, test them with real patient cases, and refine them based on results. This collaborative approach to system design ensures the final system actually reflects how your providers want to work.
Measuring the impact of collaborative CRM is important for justifying the investment and driving continued improvements. Track metrics like hospital readmission rates, medication errors caught before they harm patients, time spent on care coordination tasks, and patient satisfaction scores. Most organizations that implement collaborative CRM see improvements in all these metrics within six months of full implementation.
Pro tip: Begin your collaborative CRM rollout with a single high-volume care coordination scenario that involves multiple departments, such as pre-surgical planning or complex chronic disease management, document the improvements in patient outcomes and staff satisfaction, and then use that success story to drive adoption of collaborative workflows in other areas of your organization.
4. Strategic CRM Supporting Long-Term Patient Loyalty
Strategic CRM shifts your organization’s focus from one-time transactions to lifetime patient relationships. This system type enables you to build genuine loyalty by understanding what matters to each patient and consistently delivering personalized experiences that demonstrate you care about their wellbeing beyond their immediate medical needs.
The business case for patient loyalty is compelling. A loyal patient returns to your facility for ongoing care, refers family members and friends, and maintains continuity with your physicians even when other options become available. A patient who has visited your clinic five times over three years is far more valuable than a patient who visits once and never returns. Acquiring new patients costs significantly more than retaining existing ones. Strategic CRM helps you retain patients by making them feel valued and understood.
Unlike operational CRM that focuses on transaction efficiency or analytical CRM that focuses on data insights, strategic CRM focuses on relationship building. Your system collects information about patient preferences, communication style, family situation, lifestyle, and health beliefs. A patient might prefer email communication over phone calls. Another patient values education and wants detailed explanations of treatment options. A third patient prioritizes convenience and wants the fastest possible appointment times. When your CRM understands these individual preferences, your staff can adapt their approach accordingly. This personalization creates positive emotional connections that transform patients into loyal advocates for your healthcare facility.
Consider how this works at a large healthcare network in Abu Dhabi. Your system identifies that a patient named Fatima has diabetes and is struggling to maintain healthy blood glucose levels. Rather than simply scheduling her for periodic appointments, your strategic CRM recognizes that Fatima is a working mother with limited time and that she responds well to educational resources. Your system automatically sends her diabetes management tips via her preferred communication channel, schedules appointments at times that work with her work schedule, and connects her with other patients managing diabetes who can provide peer support. You also ensure that every interaction she has with your organization feels warm and personal. Her physicians remember details she shared in previous visits. Your clinic staff greet her by name and ask how her family is doing. You proactively reach out when you notice she has not scheduled her quarterly check-up. Over time, Fatima develops deep loyalty to your organization. When her brother needs cardiac care, Fatima refers him to your facility. When your organization launches a new women’s health program, Fatima is among the first to participate.
Data-driven segmentation is the engine that powers strategic CRM. Your system analyzes your patient population and segments them into groups based on characteristics that matter for care and loyalty. You might segment patients by age, chronic conditions, care frequency, health literacy level, or previous experience with your organization. Each segment receives tailored communication and engagement strategies. New patients with no previous healthcare relationship with you need different engagement than established patients who have been with you for ten years. Patients with multiple chronic conditions need different support than healthy patients visiting for preventive care. Your strategic CRM ensures each segment receives exactly the attention and support they need.
Earning patient loyalty in healthcare consumerism requires organizations to reduce acquisition costs and stabilize revenue through long-term relationships. Strategic CRM accomplishes this by enabling personalized engagement that builds trust over time. When patients feel genuinely cared for as individuals rather than treated as medical cases to be processed, they develop emotional loyalty that persists even when other competitors offer lower prices or newer technology.
Another critical aspect of strategic CRM is managing patient expectations and communicating your value proposition clearly. Many healthcare organizations fail to help patients understand why they should choose your facility over competitors. Your strategic CRM can systematically communicate your differentiators. If your organization has the lowest infection rates in the region, you should communicate this achievement to patients. If your physicians have the highest patient satisfaction scores, patients need to know this. If your facility specializes in treating a particular condition with exceptional results, your CRM should help patients understand why choosing your organization makes sense for their specific situation. This transparent communication builds trust and confidence.
Strategic CRM also manages the patient lifecycle. When a patient first becomes aware of your organization, they are in the awareness stage. When they select your facility for care, they move to the engagement stage. After they receive care, they move to the retention stage where the goal is ensuring they return for future care. Your strategic CRM orchestrates appropriate communication for each stage. During awareness, you educate potential patients about your capabilities and values. During engagement, you demonstrate care quality and build relationships. During retention, you maintain ongoing connection and prevent drift to competitors.
In healthcare markets across Saudi Arabia and UAE where patient expectations are rising and competition is increasing, strategic CRM becomes a differentiator. Patients increasingly choose healthcare providers based on experience and relationship quality, not just medical credentials. Your strategic CRM allows you to compete on experience. You can deliver personalized service at scale by automating personalization. Your system can manage hundreds or thousands of individual patient relationships simultaneously, ensuring each patient feels uniquely valued.
Implementing strategic CRM requires alignment across your entire organization. Your marketing team uses CRM data to craft messages that resonate with specific patient segments. Your clinical staff uses CRM insights to personalize their interactions with patients. Your patient service team uses CRM information to anticipate patient needs before patients even call. Your executive team uses CRM metrics to understand loyalty drivers and guide strategic decisions. This organizational alignment means strategic CRM is not just a technology project but a fundamental shift in how your organization operates.
Strategic CRM supports long-term loyalty by integrating patient data, enhancing communication, and facilitating personalized care pathways that build trust and satisfaction over time.
Measuring the impact of strategic CRM focuses on loyalty metrics rather than transaction metrics. Track patient retention rates, repeat visit frequency, referral rates, and patient lifetime value. Conduct patient satisfaction surveys asking whether patients feel understood and valued. Monitor patient net promoter score, which measures how likely patients are to recommend your organization. These metrics reveal whether your strategic CRM is actually building the loyalty you intended.
Pro tip: Launch your strategic CRM by selecting a single patient segment you want to build deeper loyalty with, such as patients with chronic disease or new mothers, design personalized engagement experiences specifically for that segment, measure loyalty improvements over six months, and then expand the program to other patient segments based on what you learn.
5. Cloud-Based CRM Solutions for Scalable Deployment
Cloud-based CRM systems eliminate the burden of managing complex on-premise infrastructure by hosting your patient data and workflows on remote servers accessible from anywhere with internet connectivity. This deployment model transforms how healthcare organizations scale their CRM capabilities without massive upfront capital investments in servers, storage, and IT support.
The traditional approach to CRM required your organization to purchase expensive servers, install specialized software, and maintain a dedicated IT team to manage system updates, backups, security patches, and disaster recovery. This approach created several problems. First, the capital expense was substantial. A healthcare system with multiple campuses might spend hundreds of thousands of dollars on hardware alone. Second, scaling was difficult. When you needed to add capacity, you had to purchase additional servers and wait weeks for installation and configuration. Third, maintaining security compliance was complex. Your IT team had to ensure that sensitive patient data was protected through firewalls, encryption, and access controls on systems they managed directly.
Cloud-based CRM inverts this model. A cloud vendor manages all the infrastructure, security, updates, and backups. You simply pay a monthly subscription fee and access the system through a web browser. Your organization gains immediate scalability. When patient volumes surge during flu season or when you expand to a new clinic, you can instantly scale your system by adjusting your subscription. There is no waiting for hardware installation. Your IT team shifts from managing infrastructure to managing how the system is used within your organization.
Consider how this works for a growing healthcare network in Saudi Arabia. You operate three clinics today and plan to open five more clinics over the next two years. With an on-premise CRM, you would need to purchase additional servers to handle the patient data from new clinics, install them, configure them, and integrate them with your existing system. This process might take three to four months per new clinic. With a cloud-based CRM, you simply add new users to your subscription. The cloud vendor automatically scales server capacity behind the scenes. Your new clinics can go live within weeks, not months. All clinics access the same patient database simultaneously, creating seamless continuity of care across your entire network.
Cloud-based systems excel at enabling remote access. This became critical during pandemic lockdowns, but remains important in normal operations. Your physicians can access patient records from home, from other hospitals, or from any location with internet access. Your care coordinators can work from the office or remotely. Your patient service team can manage calls from anywhere. This flexibility improves work-life balance for your staff and allows you to recruit talent across broader geographic areas. A nurse manager in Dubai can access the same real-time data as a nurse manager in Jeddah, enabling better coordination across your network.
Cloud-based CRM systems centralize customer data and automate workflows without requiring local IT infrastructure, integrate easily with existing tools, support HIPAA compliance, and offer automated reminders and patient engagement features suitable for growing healthcare organizations. This integration capability is particularly valuable. Your cloud-based CRM can connect with your electronic health record system, your laboratory information system, your billing system, and your patient communication platform. Rather than forcing data to flow through multiple systems and creating silos of information, cloud integration creates a unified data ecosystem where information flows seamlessly.
Security and compliance are handled by the cloud vendor according to industry standards. Reputable cloud CRM vendors maintain HIPAA compliance certifications, perform regular security audits, encrypt data in transit and at rest, and maintain redundant systems across multiple geographic locations for disaster recovery. Your organization benefits from security expertise that would be extremely expensive to build in-house. The cloud vendor’s entire business depends on protecting customer data, so they invest heavily in security measures that most individual healthcare organizations could not afford to implement independently.
Cost structure represents another major advantage. With on-premise CRM, you pay a large upfront capital expense, then ongoing costs for maintenance, updates, and support. With cloud CRM, you pay predictable monthly subscription fees with no capital expense. This allows you to invest capital in clinical services rather than IT infrastructure. For a growing healthcare organization, this shift from capital expense to operational expense makes financial sense.
Scalability also applies to user growth. Your organization might start with 50 CRM users and grow to 500 users over five years. Cloud systems scale to thousands or tens of thousands of users without degradation in performance. You do not need to worry about whether your system can handle the growth. The cloud vendor manages that infrastructure scaling transparently.
Another benefit is continuous updates without system downtime. When your cloud vendor releases new features or security patches, they deploy these updates to your system automatically without requiring your IT team to perform anything. You always have access to the latest functionality and security improvements. Compare this to on-premise systems where updates require scheduled maintenance windows that take your system offline.
For healthcare organizations in the UAE managing multiple facilities, cloud-based CRM enables unified data governance. Patient records follow patients across your network seamlessly. A patient who visits your clinic in Abu Dhabi, then receives specialist care at your hospital in Dubai, then follows up at your clinic in Sharjah has a single unified record that all three locations access. This continuity improves patient safety because every provider sees the complete clinical picture.
Cloud-based systems support scalable deployment of CRM functionalities by allowing healthcare providers to continuously monitor patients, share data securely, and coordinate care remotely thereby improving outcomes and operational efficiencies in healthcare delivery.
Implementing cloud-based CRM does require attention to workflow design and change management. Your organization must define which business processes will run in the cloud and how those processes will integrate with existing systems. This is where low-code platforms become valuable. Rather than extensive custom coding, you can use visual workflow designers to map your processes. If you need to modify a workflow after implementation, you can make changes without writing code or waiting for developer availability.
One consideration is data migration. Moving from your existing CRM or from paper records to cloud-based CRM requires careful planning. You must ensure data accuracy, maintain security throughout the migration process, and minimize disruption to ongoing operations. Most cloud vendors provide migration services that handle these complexities. Planning for a three to six month migration timeline allows sufficient time for thorough data validation.
Bandwidth and internet connectivity requirements are minimal for cloud CRM. Unlike some cloud applications that require constant data synchronization, CRM systems are relatively lightweight. Users with standard broadband connections experience responsive performance.
Pro tip: When evaluating cloud-based CRM vendors, request a trial environment where your team can test workflows specific to your organization before committing to a contract, use that trial period to identify integration requirements and workflow customizations, and select a vendor whose architecture and pricing model support your growth projections for the next three to five years.
6. On-Premise CRM for Enhanced Data Security
On-premise CRM systems run on servers physically located within your healthcare facility, giving your organization direct control over patient data and cybersecurity infrastructure. This deployment model appeals to healthcare organizations that prioritize maximum security control and regulatory compliance over the convenience of cloud accessibility.
The security advantage of on-premise CRM is straightforward. Your patient data never leaves your facility. It does not travel across the internet to external servers. It does not sit in data centers managed by third-party vendors. Your organization maintains complete physical and administrative control over sensitive patient information. For a healthcare system managing hundreds of thousands of patient records containing detailed medical histories, genetic information, and behavioral health data, this level of control provides significant peace of mind.
Understanding why data security matters in healthcare requires recognizing what attackers target. Patient medical records are worth far more on the dark web than credit card numbers. A single complete patient record with medical history, medications, allergies, and social security number can sell for $50 to $250 depending on the data completeness. An attacker who breaches a healthcare system with 100,000 patients could potentially profit millions of dollars while destroying the trust patients place in that organization. Healthcare cybersecurity challenges continue escalating as advanced persistent threats target healthcare institutions worldwide with increasing sophistication.
On-premise CRM systems limit your exposure to external cyber threats by design. Your system does not rely on internet connectivity to function. You can operate your CRM even if your internet connection fails. Your data does not depend on a cloud vendor’s security posture. You do not assume risk related to data breaches at cloud vendors that might impact thousands of organizations simultaneously. This architectural advantage appeals to healthcare leaders who have experienced or studied major healthcare data breaches and recognize the costs of those incidents.
Consider a healthcare scenario in Saudi Arabia where your organization manages sensitive patient data including psychiatric records and HIV status information. Regulatory requirements may mandate that this data remain within your national borders and under your direct control. An on-premise CRM allows you to meet these requirements without relying on vendors or cloud providers operating outside your jurisdiction. You maintain sovereignty over your data.
Your organization controls access to your CRM system through physical security and network architecture. You can restrict access to your CRM to computers physically connected to your internal network. You can require VPN authentication for remote access. You can implement badge access controls on the server room where your CRM hardware lives. You control firewall rules that determine which external systems can communicate with your CRM. This granular control prevents unauthorized external access in ways that cloud systems cannot fully replicate.
Another security advantage is visibility into your system’s operations. You can audit every access to your CRM database. You can see exactly which users accessed which patient records and when. You can set up alerts that notify security teams if unusual access patterns occur. You can review your security logs yourself rather than relying on a vendor’s security reports. This transparency helps you identify and respond to security threats quickly.
Implementing on-premise CRM successfully requires investment in security infrastructure and personnel. You need firewalls, intrusion detection systems, data encryption, and regular security assessments. You need cybersecurity professionals on your staff or on contract who understand healthcare security requirements. You need backup systems and disaster recovery planning. These investments are substantial but provide direct protection for your most valuable asset: patient data.
Regulatory compliance becomes more straightforward with on-premise systems. HIPAA compliance, data breach notification requirements, and other healthcare regulations focus on ensuring that patient data is protected. When your organization manages your own infrastructure, you control the security controls that demonstrate compliance. You do not need to verify that a cloud vendor meets your compliance requirements. You do not need to include vendor security agreements in your regulatory documentation. You implement compliance directly.
Disaster recovery planning is under your direct control with on-premise CRM. You decide how frequently to back up your data. You decide where to store backup copies. You decide how quickly your organization can recover from a hardware failure or catastrophic data loss. You can test disaster recovery procedures yourself without depending on vendor support. This control over your own resilience is valuable for healthcare organizations where system downtime directly impacts patient care.
For healthcare systems in the UAE managing critical infrastructure, on-premise CRM may be required by national security policies. Government healthcare facilities often mandate on-premise systems to ensure that critical health infrastructure remains under direct government control. This is not merely a technology choice but a strategic decision aligned with national security considerations.
On-premise CRM systems limit data exposure to external environments and offer direct control over cybersecurity protocols, however they require significant investment in security infrastructure and personnel to defend against advanced persistent threats targeting healthcare institutions worldwide.
One important consideration is the total cost of ownership for on-premise systems. The purchase price of CRM software is often lower than cloud subscription costs, but this advantage can disappear when you account for hardware costs, ongoing maintenance, security personnel, backup infrastructure, and facility space. An organization with 200 CRM users might spend $300,000 to $500,000 annually on on-premise CRM when all costs are included. Compare this to potential cloud costs that might range from $200,000 to $400,000 annually depending on functionality required. The economics depend on your specific situation.
Another consideration is staff burden. On-premise CRM requires dedicated IT personnel to manage updates, patches, hardware maintenance, backups, and disaster recovery. Your IT team must develop expertise in your specific CRM platform. When vendors release new versions, your team must test them, plan for upgrades, and manage the upgrade process without service interruption. This ongoing burden can strain smaller IT departments.
On-premise CRM also requires careful capacity planning. You must purchase hardware with sufficient capacity to handle your expected patient volume for several years. Purchasing excess capacity wastes capital. Purchasing insufficient capacity forces expensive upgrades. With cloud systems, capacity adjusts automatically. With on-premise systems, you must make capacity predictions years in advance.
Despite these considerations, for healthcare organizations with strong security requirements, sophisticated IT teams, and commitment to data sovereignty, on-premise CRM provides unmatched control and protection. Your organization can design your security architecture precisely as your risk profile requires. You can respond quickly to emerging threats without waiting for vendor patches. You maintain complete transparency into how your patient data is protected.
Pro tip: If you choose on-premise CRM, establish a cybersecurity governance committee that reviews security logs monthly, conducts penetration testing annually, updates security protocols based on emerging threats, and ensures your IT team stays current with the latest healthcare security best practices through training and certifications.
7. Industry-Specific CRM for Healthcare Needs
Industry-specific CRM systems are purpose-built for healthcare organizations, incorporating features and compliance requirements that general business CRM software simply does not support. These specialized platforms understand the unique complexity of healthcare workflows and integrate seamlessly with clinical systems that hospitals and clinics depend on daily.
The critical difference between healthcare CRM and generic CRM becomes clear when you examine what healthcare organizations actually need. A general CRM designed for sales teams might excel at managing opportunities and closing deals, but it lacks features for managing patient intake forms, scheduling clinical appointments, or integrating with electronic health record systems. A healthcare-specific CRM, by contrast, is built from the ground up with healthcare workflows in mind.
Consider what happens when a patient calls your clinic to schedule an appointment. Your receptionist needs to access the patient’s insurance information, verify that it is current, check for any medication allergies, review recent visit notes, and confirm that the patient has completed required pre-visit paperwork. A generic CRM might have some contact management capabilities, but it would not integrate with your EHR system to retrieve clinical information or with your insurance verification system to confirm coverage in real-time. A healthcare-specific CRM handles all of this seamlessly. Your receptionist sees a unified patient profile that pulls information from multiple systems automatically.
Compliance with healthcare regulations is another area where industry-specific systems excel. HIPAA compliance requires that your CRM enforce access controls, maintain audit trails, encrypt patient data, and support secure communication. Healthcare CRM systems are tailored to meet industry-specific requirements such as HIPAA compliance, integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs), clinical decision support, and service automation. These specialized platforms support patient intake, scheduling, remote monitoring, and care coordination, addressing healthcare complexities that general CRMs do not accommodate. A healthcare CRM has these compliance features built in. A generic CRM requires significant customization and ongoing vigilance to maintain compliance.
Remote patient monitoring represents another area where healthcare-specific CRM adds tremendous value. Your organization might monitor patients with chronic diseases using connected devices that track blood pressure, glucose levels, or heart rate. Healthcare-specific CRM systems can integrate with these devices, automatically capture readings, flag abnormal values, and alert appropriate clinicians. A generic CRM has no awareness that this data even exists.
Clinical decision support is another healthcare-specific feature. Your CRM can integrate with clinical guidelines and alert your physicians when a patient’s treatment plan deviates from evidence-based protocols. If a patient with diabetes and hypertension is not on an ACE inhibitor, your system can alert the physician that this class of medication is recommended for this patient population. Generic CRMs have no ability to understand clinical guidelines.
In healthcare organizations across Saudi Arabia and UAE, industry-specific CRM becomes even more valuable. Your system can support multilingual interfaces in Arabic and English. It can accommodate cultural preferences in how patients prefer to be communicated with. It can integrate with local insurance systems and government health initiatives. A generic CRM would require extensive customization to meet these regional needs.
Patient engagement workflows also benefit from healthcare-specific design. Your CRM can manage automated appointment reminders via SMS and email in the patient’s preferred language. It can send post-visit surveys to gather feedback on care quality. It can provide patients with educational resources appropriate to their diagnosis. It can support secure patient portals where patients view test results and communicate with their care team. These workflows are standard features in healthcare CRM but would require custom development in generic systems.
Another advantage is that healthcare-specific CRM platforms understand the various healthcare provider types. A system designed for hospitals handles different workflows than a system designed for ambulatory clinics or specialty practices. A system for a large health system with multiple campuses must handle different processes than a small private practice. Quality healthcare CRM vendors have built their systems to accommodate these variations without requiring massive customization.
Integration with other healthcare systems is critical. Your CRM must connect with your EHR, your practice management system, your billing system, your patient communication platform, and potentially your revenue cycle management system. Healthcare-specific CRM platforms have pre-built connectors to common healthcare systems. Your IT team can implement these integrations in weeks rather than months. Compare this to attempting to integrate a generic CRM with your healthcare systems, which would require custom development and ongoing maintenance.
Reporting and analytics also differ between generic and healthcare-specific CRM. Healthcare organizations need reports on patient outcomes, clinical quality metrics, referral patterns, and care coordination effectiveness. Generic CRM platforms report on sales activities and customer acquisition costs. Healthcare CRM platforms report on metrics that matter to healthcare leaders like readmission rates, patient satisfaction scores, and population health measures.
For medical device companies and pharmaceutical organizations operating in the healthcare space, specialized CRM systems manage relationships with healthcare providers differently than generic systems. These platforms track key opinion leaders, manage continuing medical education requirements, and ensure compliance with regulations governing industry-provider relationships.
Healthcare CRM systems address healthcare complexities that general CRMs do not accommodate, thus enhancing provider workflows and patient outcomes.
Staff training is another area where healthcare-specific CRM shines. Your users already understand healthcare concepts and workflows. A healthcare-specific CRM uses terminology and processes they recognize immediately. A generic CRM requires significant training because users must learn unfamiliar terminology and adapt workflows to how the system works rather than how healthcare actually works. This difference dramatically affects user adoption. Staff members embrace systems that work the way they naturally work. They resist systems that force them to change their processes.
For healthcare CIOs evaluating CRM systems, industry-specific solutions should be your primary focus. While they may cost more than generic alternatives initially, the total cost of ownership is typically lower because they require less customization and integrate more easily with your existing healthcare systems. User adoption is higher because staff members recognize familiar healthcare workflows. Compliance is simpler because healthcare-specific features handle regulatory requirements built-in. Patient outcomes improve because clinical decision support and care coordination features are purpose-built for healthcare.
When selecting an industry-specific healthcare CRM, evaluate whether the vendor has deep healthcare expertise. Do they have healthcare clients you can reference? Do their product roadmaps align with emerging healthcare trends? Do they actively participate in healthcare industry associations and conferences? These indicators suggest a vendor committed to the healthcare market.
Pro tip: When evaluating industry-specific healthcare CRM systems, request demonstrations focused on your organization’s highest-pain workflows such as patient intake, appointment scheduling, or post-discharge follow-up, then verify that the system’s native features handle these workflows without requiring customization, which indicates the platform truly understands healthcare needs rather than being a generic system with healthcare features added.
Below is a comprehensive table summarizing the various types of CRM systems discussed in the article and their respective applications in healthcare.
| CRM Type | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Operational CRM | Focuses on automating and managing everyday interactions with patients, such as appointment scheduling and follow-ups. | Reduces administrative burden, improves appointment management, and ensures a seamless patient experience. |
| Analytical CRM | Utilizes patient data to analyze trends and improve care delivery through actionable insights and predictions. | Reveals hidden trends, supports evidence-based decision-making, and predicts patient risks for preventative intervention. |
| Collaborative CRM | Facilitates communication and coordination among care team members by centralizing patient information and workflows. | Reduces care fragmentation, enhances provider accountability, and ensures better patient outcomes. |
| Strategic CRM | Focuses on building long-term patient relationships through personalized care and engagement strategies. | Enhances patient loyalty, personalizes engagement, and optimizes patient lifecycle management. |
| Cloud-Based CRM | Hosted on remote servers, allowing for scalable deployment and improved accessibility. | Scales with organizational growth, reduces infrastructure costs, and enables remote staff access. |
| On-Premise CRM | Operates within the healthcare facility’s servers, providing enhanced control over patient data management. | Ensures data security, complies with stringent regulations, and provides direct oversight of IT operations. |
| Industry-Specific CRM | Tailored for healthcare workflows and integrates seamlessly with clinical systems. | Addresses unique healthcare complexities, ensures compliance, and supports patient engagement. |
Elevate Healthcare CRM with Singleclic’s Expertise
Healthcare CIOs face complex challenges in selecting and implementing the right CRM systems to streamline operations, enhance patient engagement, and ensure data security. This article highlights key CRM types from operational and analytical to collaborative and strategic, each designed to optimize specific areas such as appointment management, care coordination, and long-term patient loyalty. Pain points like fragmented communication, data silos, security concerns, and workflow rigidity can undermine care quality and organizational efficiency. Addressing these issues requires tailored, scalable CRM solutions that integrate seamlessly with healthcare workflows.
At Singleclic, we specialize in delivering end-to-end Digital Transformation and ERP/CRM Implementation services across the KSA, UAE, and Egypt healthcare sectors. Our solutions leverage cutting-edge platforms like Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Odoo combined with our Arabic-enabled, on-premise low-code platform, Cortex, empowering healthcare providers to design, automate, and optimize complex processes without writing code. Whether your needs include operational automation, advanced analytics, or secure cloud and on-premise deployments, Singleclic tailors CRM systems to your unique challenges — ensuring improved patient satisfaction, data governance, and sustainable growth.

Discover how Singleclic can transform your healthcare CRM strategy today. Visit Singleclic to learn about our comprehensive solutions and start building a patient-centric, efficient, and secure healthcare organization now. Take the next step toward seamless care coordination and data-driven decision-making with trusted partners who understand your industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of CRM systems are essential for healthcare organizations?
Operational, Analytical, Collaborative, Strategic, Cloud-Based, On-Premise, and Industry-Specific CRM systems are essential for healthcare organizations. Understanding each type allows CIOs to select the right system that aligns with their organizational goals and improves patient care.
How can Operational CRM improve patient interactions?
Operational CRM enhances patient interactions by automating routine tasks such as appointment scheduling and follow-ups, which improves efficiency. By implementing this system, healthcare facilities can reduce no-show rates by approximately 20% through automated reminders.
What benefits does Analytical CRM provide in a healthcare setting?
Analytical CRM transforms patient data into actionable insights, allowing organizations to make proactive decisions regarding patient care. Hospitals can use this system to identify patterns, such as predicting which patients are at risk for readmission, enabling targeted interventions within 30 days.
How does Collaborative CRM enhance care coordination?
Collaborative CRM facilitates communication among different departments, ensuring all healthcare providers access the same patient information in real time. This coordination significantly reduces care fragmentation and can lead to improved patient outcomes, with measurable reductions in emergency visits.
What investment considerations should CIOs be aware of when implementing CRM systems?
CIOs must consider both initial costs and long-term operational impacts when implementing CRM systems. For example, investing in a Cloud-Based CRM may involve lower upfront expenses but requires ongoing subscription fees, whereas On-Premise systems may have higher initial costs with predictable ongoing maintenance expenses.
Why is Industry-Specific CRM important for healthcare?
Industry-Specific CRM systems are crucial as they cater to the unique workflows and compliance requirements of healthcare organizations. Utilize this type of CRM to streamline workflows and improve patient management within a few months of implementation.